Retirement Guide for UPS Employees
2024 Tax Rates & Inflation
In our comprehensive retirement guide for UPS employees, we go through many factors which you may take into account when deciding on the proper time to retire from UPS. Some of those factors include: healthcare & benefit changes, interest rates, the new 2024 tax rates, inflation, and much more. Keep in mind we are not affiliated with UPS, and we recommend reaching out to your Corporate benefits department for further information.
Table of Contents
2024 Tax Changes & Inflation

It is imperative for individuals to be aware of new changes made by the IRS. The main factors that will impact employees will be the following:
- The 2024 standard deduction will increase to $14,600 for single filers and those married filing separately, $29,200 for joint filers, and $21,900 for heads of household.
- Taxpayers who are over the age of 65 or blind can add an additional $1,550 to their standard deduction. That amount jumps to $1,950 if also unmarried or not a surviving spouse.
Retirement account contributions: Contributing to your company's 401k plan can cut your tax bill significantly, and the amount you can save has increased for 2024. The amount individuals can contribute to their 401(k) plans in 2024 will increase to $23,000 -- up from $22,500 for 2023. The catch-up contribution limit for employees age 50 and over will increase to $7,500.
There are important changes for the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) that you, as a taxpayer employed by a corporation, should know:
- The tax year 2024 maximum Earned Income Tax Credit amount is $7,830 for qualifying taxpayers who have three or more qualifying children, up from $7,430 for tax year 2023.
- Married taxpayers filing separately can qualify: You can claim the EITC as married filing separately if you meet other qualifications. This was not available in previous years.
Deduction for cash charitable contributions: The special deduction that allowed single nonitemizers to deduct up to $300—and married filing jointly couples to deduct $600— in cash donations to qualifying charities has expired.
Child Tax Credit changes:
- The maximum tax credit per qualifying child is $2,000 for children five and under – or $3,000 for children six through 17 years old. Additionally, you can't receive a portion of the credit in advance, as was the case in 2023.
- As a parent or guardian, you are eligible for the Child Tax Credit if your adjusted gross income is less than $200,000 when filing individually or less than $400,000 if you're filing a joint return with a spouse.
- A 70 percent, partial refundability affecting individuals whose tax bill falls below the credit amount.
2024 Tax Brackets

Inflation reduces purchasing power over time as the same basket of goods will cost more as prices rise. In order to maintain the same standard of living throughout your retirement after leaving your company, you will have to factor rising costs into your plan. While the Federal Reserve strives to achieve a 2% inflation rate each year, in 2023 that rate shot up to 4.9% which was a drastic increase from 2020’s 1.4%. While prices as a whole have risen dramatically, there are specific areas to pay attention to if you are nearing or in retirement from your company, like healthcare.
It is crucial to take all of these factors into consideration when constructing your holistic plan for retirement from your company.
*Source: IRS.gov, Yahoo, Bankrate, Forbes
Schedule An Appointment with a Retirement Group Advisor
Please choose a date that works for you from the available dates highlighted on the calendar.
Recent Layoff Announcements & Other UPS News
Planning Your Retirement

Retirement planning is a verb; consistent action must be taken whether you’re 20 or 60.
The truth is that most Americans don’t know how much to save or the amount of income they’ll need.
No matter where you stand in the planning process, or your current age, we hope this guide provides you a good overview of the steps to take and resources that help you simplify your transition from your company into retirement and get the most from your benefits.
You know you need to be saving and investing, especially since time is on your side the sooner you start, but you don’t have the time or expertise to know if you’re building retirement savings that can last after leaving your company.
"A separate study by Russell Investments, a large money management firm, came to a similar conclusion. Russell estimates a good financial advisor can increase investor returns by 3.75 percent."
Source: Is it Worth the Money to Hire a Financial Advisor? The Balance, 2021
Starting to save as early as possible matters. Time on your side means compounding can have significant impacts on your future savings. And, once you’ve started, continuing to increase and maximize your contributions for your 401(k) plan is key.

There's a 79% potential boost in wealth at age 65 over a 20-year period when choosing to invest in your company's retirement plan.
*Source: Bridging the Gap Between 401(k) Sponsors and Participants, T.Rowe Price, 2020
As decades go by, you’re likely full swing into your career at your company and your income probably reflects that. However, the challenges of saving for retirement start coming from large competing expenses: a mortgage, raising children, and saving for their college.
One of the classic planning conflicts is saving for retirement versus saving for college. Most financial planners will tell you that retirement from your company should be your top priority because your child can usually find support from financial aid while you’ll be on your own to fund your retirement.
How much we recommend that you invest towards your retirement is always based on your unique financial situation and goals. However, consider investing a minimum of 10% of your salary toward retirement through your 30s and 40s.
As you enter your 50s and 60s, you’re ideally at your peak earning years with some of your major expenses, such as a mortgage or child-rearing, behind you or soon to be in the rearview mirror. This can be a good time to consider whether you have the ability to boost your retirement savings goal to 20% or more of your income. For many people, this could potentially be the last opportunity to stash away funds.
In 2024, workers age 50 or older can invest up to $23,000 into their retirement plan/401(k), and once they meet this limit, they can add an additional $7,500 in catch-up contributions for a combined annual total of $30,500. These limits are adjusted annually for inflation.
Why are 401(k)s and matching contributions so popular?
These retirement savings vehicles give you the chance to take advantage of three main benefits:
- Compound growth opportunities (as seen above)
- Tax saving opportunities
- Matching contributions
Matching contributions are just what they sound like: your company matches your own 401(k) contributions with money that comes from the company. If your company matches, the company money typically matches up to a certain percent of the amount that you put in.
Unfortunately, many people fail to take advantage of their company's matching contributions because they’re not contributing the required minimum to receive the full company match.
According to Bank of America's "2022 Financial Life Benefit Impact Report", despite 58% of eligible employees participating in a 401(k) plan, 61% of them contributed less than $5,000 during the current year.
The study also found that fewer than one in 10 participants’ contributions reached the ceiling on elective deferrals, under IRS Section 402(g) — which is $23,000 for 2024.
A 2020 study from Financial Engines titled “Missing Out: How Much Employer 401(k) Matching Contributions Do Employees Leave on the Table?”, revealed that employees who don’t maximize their company match typically leaves $1,336 of extra retirement money on the table each year.
For example, if your company will match up to 3% of your plan contributions and you only contribute 2% of your salary, you aren’t getting the full amount of the company match. By simply increasing your contribution by just 1%, your company is now matching the full 3% of your contributions for a total combined contribution of 6%. By doing so, you aren’t leaving money on the table.
Your Pension Plan

UPS Teamsters Pension
The UPS Teamsters Pension Plan offers retirement benefits for both part-time and full-time employees. The pension benefits are calculated based on years of credited service and a benefit formula that varies depending on the employee's status and service duration. Here's a detailed explanation of the pension formula and how it works:
Part-Time Employees
Benefit Formula:
August 1, 2004 - July 31, 2008: $55 per year of credited service, up to 35 years.
August 1, 2008 - July 31, 2023: $60 per year of credited service, up to 35 years.
Effective August 1, 2023: $65 per year of credited service, up to 35 years.
Credited Service Requirements:
One year of credited service is earned with 750 or more paid hours in a calendar year.
Six months of credited service for 375-500 hours worked.
Nine months of credited service for 501-749 hours worked.
Monthly Service Pension Benefits:
$2,450 for retirement at any age after 35 years of part-time credited service.
$2,100 for retirement at any age after 30 years of part-time credited service.
$1,750 for retirement at age 60 with 25 years of part-time credited service.
$1,450 for retirement at any age with 25 years of part-time credited service (based on $58.00 per year of credited service).
Full-Time Employees
Benefit Formula:
January 1, 2024 and beyond: $185 per month for each year of future service, up to a maximum of 35 years of credited service.
Eligibility and Vesting:
Employees become participants on the first day of the month coincident with or immediately following the date they meet the eligibility criteria.
Early retirement benefits can begin at age 50 with five years of vesting service, with a 6% reduction per year for each year prior to normal retirement age (65 years).
Calculation Example
Part-Time Employee
Assume a part-time employee has worked for 30 years with 750 or more hours each year, retiring in 2024:
Years of Credited Service: 30 years.
Benefit Formula (post-2023): $65 per year of credited service.
Monthly Pension: 30 x $65 = $1,950/per month
Full-Time Employee
Assume a full-time employee works 35 years and retires in 2025:
Years of Credited Service: 35 years.
Benefit Formula (2025): $185 per month per year of credited service.
Monthly Pension: 35 x $185 = $6,475/per month
UPS Management Pension Plan
The UPS Management Pension Plan is designed to provide retirement benefits to eligible employs based on their years of service and compensation. Here's a detailed explanation of how the pension formula works, sourced from the "UPS Retirement Plan, as Amended and Restated" document.
Pension Formula
The UPS Retirement Plan calculates retirement benefits using a defined benefit formula, which primarily considers a participant's years of service and their Final Average Compensation (FAC).
Final Average Compensation (FAC)
Definition: FAC is the average annual compensation for the highest consecutive five full calendar years out of the last ten years of employment. If a participant has fewer than five years of service, all available years are used(UPS Retirement Plan, as…).
Compensation Limits: The plan considers only the compensation up to the applicable dollar limits set by Section 401(a)(17) of the Internal Revenue Code, which includes cost-of-living adjustments.
Benefit Service
Definition: Benefit Service refers to the credited years of service that count towards the pension calculation. Participants accrue Benefit Service for each year they work for UPS, contributing to the pension plan.
Early Retirement: Participants can opt for early retirement benefits if they meet certain age and service requirements, but the benefits are reduced based on specific factors. For instance, with less than 20 years of Benefit Service, the reduction is 0.5% for each month the retirement date precedes the normal retirement date. With 20 or more years, the reduction is 0.25% per month.
Calculation of Pension Benefits
The retirement benefit is calculated using the following formula:
Annual Pension Benefit = FAC × Benefit Multiplier × Years of Benefit Service
Benefit Multiplier: This is a fixed percentage that varies based on the specifics of the plan and the employee's service category. For example, the RPA Formula might have different multipliers compared to the UPS Freight Formula.
Example Calculation
Assuming a participant has the following details:
Final Average Compensation (FAC): $80,000
Years of Benefit Service: 25 years
Benefit Multiplier: 1.5%
The annual pension benefit would be calculated as: $80,000 × 0.015 × 25 = $30,000
This means the participant would receive an annual pension benefit of $30,000.
Age Penalties and Reductions in the UPS Pension Defined Benefit Plan
The UPS Pension Defined Benefit Plan, specifically for final average pay, incorporates various age-related penalties and reductions to ensure fair distribution of pension benefits based on the employee's age at the time of retirement. These penalties and reductions aim to balance the actuarial value of the pension across different retirement ages.
Key Aspects of Age Penalties and Reductions:
1. Early Retirement Reduction:
Employees who retire before reaching the plan's normal retirement age (usually 65) are subject to an early retirement reduction. This reduction is applied to account for the longer period over which benefits will be paid.
2. Normal Retirement Age:
The normal retirement age is typically 65. Retiring at this age allows employees to receive their full accrued benefit without any reductions.
3. Reduction Factors:
The reduction factors are calculated based on actuarial principles to ensure the pension's present value remains consistent regardless of the retirement age. Typically, these factors reduce the monthly benefit by a specific percentage for each year an employee retires before the normal retirement age.
Example Calculation:
Scenario: An employee, John, retires at age 60 with 30 years of service. His final average pay is $100,000.
Step-by-Step Calculation:
1. Determine Accrued Benefit:
* Assume the plan formula provides 1.5% of final average pay per year of service.
* Accrued Benefit = 1.5% × 30 years × $100,000 = $45,000 annually.
2. Apply Early Retirement Reduction:
* The reduction factor might be 5% per year for retirement before age 65.
* John is retiring 5 years early, so the total reduction = 5% × 5 = 25%.
3. Calculate Reduced Benefit:
* Reduced Benefit = Accrued Benefit × (1 - Reduction Percentage)
* Reduced Benefit = $45,000 × (1 - 0.25) = $45,000 × 0.75 = $33,750 annually.
Special Rules
Grandfathered Participants: Employees who were part of the plan before certain amendments have special provisions to ensure their benefits are not less than what they would have accrued under previous rules.
Benefit Adjustments: For participants from merged companies (like Overnite Transportation), special rules apply to ensure a fair calculation based on their unique service records and compensation histories.
UPS Stock Options and Restricted Stock Units (RSUs)
UPS provides various stock-based incentives to its employees as part of its Management Incentive Program (MIP). These incentives are designed to align the interests of employees with those of the shareholders by giving employees an ownership stake in the company. The two primary forms of stock-based incentives offered by UPS are stock options and Restricted Stock Units (RSUs).
Stock Options
Stock Options grant employees the right to purchase a certain number of shares at a predetermined price, known as the exercise price, after a specified period. The key elements of stock options include:
1. Grant Date: The date on which the stock options are awarded.
2. Exercise Price: The price at which employees can purchase the stock, typically set at the market price on the grant date.
3. Vesting Period: The period employees must wait before they can exercise their options.
4. Expiration Date: The last date on which employees can exercise their options.
Employees benefit from stock options if the market price of the stock exceeds the exercise price at the time of exercising the options.
Restricted Stock Units (RSUs)
Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) are company shares given to employees as part of their compensation. The key features of RSUs include:
1. Grant Date: The date on which the RSUs are awarded.
2. Vesting Schedule: The period over which the RSUs vest, meaning they become the property of the employee. This schedule can be based on tenure or performance milestones.
3. Delivery of Shares: Upon vesting, the employee receives the shares or the cash equivalent, depending on the company's policies.
RSUs provide employees with an ownership interest in the company once they vest, and they are often used to retain employees by incentivizing them to stay with the company until the RSUs vest.
Calculation Example for RSUs
Scenario: An employee, John, receives a grant of 100 RSUs on January 1, 2020. The RSUs vest over four years, with 25% vesting each year.
1. Grant Details:
* Grant Date: January 1, 2020
* Number of RSUs: 100
* Vesting Schedule: 25% per year over four years
2. Vesting Calculation:
* 25 RSUs vest on January 1, 2021
* 25 RSUs vest on January 1, 2022
* 25 RSUs vest on January 1, 2023
* 25 RSUs vest on January 1, 2024
3. Market Value:
* Assume the market value of UPS shares is $150 on the vesting dates.
4. Total Value:
* 2021: 25 RSUs × $150 = $3,750
* 2022: 25 RSUs × $150 = $3,750
* 2023: 25 RSUs × $150 = $3,750
* 2024: 25 RSUs × $150 = $3,750
Eligibility
Eligibility for stock options and RSUs under the UPS Management Incentive Program (MIP) is determined based on the employee's role and performance. The eligibility criteria are as follows:
1. Management Committee Members: These employees are directly approved by the Committee and receive performance incentive awards and ownership incentive awards, including RSUs(UPS MIP).
2. Other Eligible Employees: Employees classified at the supervisor level or above on the MIP Record Date and recommended by their managers are considered for awards. They can receive RSUs and other incentives based on their classification and performance(UPS MIP).
UPS 409A Deferred Compensation & Executive Compensation Supplemental Savings Plan
The UPS 409A Deferred Compensation Plan and the Executive Compensation Supplemental Savings Plan are designed to provide eligible employees with opportunities to defer compensation and accumulate savings for retirement. These plans adhere to the regulations outlined in Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code, which governs non-qualified deferred compensation plans.
Eligibility:
Eligible Employees: Typically includes management and highly compensated employees who meet the criteria set forth by the UPS Salary Committee.
Key Features:
1. Deferral Elections:
* Eligible employees can elect to defer a portion of their salary, bonuses, or other eligible compensation before the beginning of the Plan Year during which the compensation is earned.
2. Vesting:
* The deferral amounts are vested according to the plan's terms, which may vary based on the employee's role and tenure with UPS.
3. Distribution Options:
* Distributions from the deferred compensation accounts can be made upon specific events such as separation from service, disability, death, or at a specified date or schedule elected by the participant. These distributions must comply with the 409A regulations to avoid penalties.
4. Tax Treatment:
* Deferred amounts are not subject to federal income tax until distributed. However, they are subject to Social Security and Medicare taxes when deferred.
Executive Compensation Supplemental Savings Plan
Eligibility:
Executive Leadership Team: Includes senior executives and members of the UPS Management Committee, who are approved for participation by the Compensation Committee.
Key Features:
1. Supplemental Contributions:
* In addition to deferral elections, UPS may make supplemental contributions to the accounts of eligible executives. These contributions are determined based on performance and other criteria established by the Compensation Committee.
2. Vesting and Forfeiture:
* Supplemental contributions typically vest based on continued employment or achievement of specific performance goals. Unvested amounts may be forfeited if the executive leaves the company before meeting the vesting requirements.
3. Payout Options:
* Similar to the Deferred Compensation Plan, payouts from the Supplemental Savings Plan can occur upon separation from service, death, disability, or other specified times elected by the participant. The timing and form of payments must comply with Section 409A to avoid adverse tax consequences.
Example Calculation and Audit
Scenario: An executive, Sarah, elects to defer $50,000 of her 2023 salary. Additionally, UPS makes a supplemental contribution of $20,000 to her account.
1. Deferral:
* Elective Deferral: $50,000
* Supplemental Contribution: $20,000
2. Vesting and Account Balance:
* Assume both amounts are fully vested by the end of 2023.
* Total Deferred Compensation: $50,000 + $20,000 = $70,000
3. Interest Credits:
* If the account earns 5% interest annually, the interest for 2023 would be:
* Interest = $70,000 × 5% = $3,500
* Year-End Balance = $70,000 + $3,500 = $73,500
4. Distribution:
* If Sarah elects to receive her balance upon retirement in 2025, assuming no further contributions and a continued 5% annual interest:
* 2024 Balance: $73,500 × 1.05 = $77,175
* 2025 Balance: $77,175 × 1.05 = $81,033.75
Your 401(k) Plan

UPS 401(k) Savings Plan (effective 1/1/2023)
Employees are encouraged to enroll in a 401(k) savings plan right away. UPS has implemented a number of enhancements to the 401(k) Savings Plan, effective January 1, 2023. The enhanced 401(k) Plan is designed to help support the retirement savings needs of UPSers now and into the future.
SavingsPLUS Match
The SavingsPLUS match formula has become simplified. All eligible active UPSers are eligible for the same match amount regardless of hire date or years of service.
Each quarter, UPS will match 50% of your personal pre-tax and/or Roth 401(k) and/or regular after-tax contributions to the 401(k) Plan, up to 6% of your eligible compensation1
(that’s a maximum match contribution of 3%).
Employees must make personal contributions to the 401(k) Plan to receive the SavingsPLUS match.
The SavingsPLUS match will no longer be provided in UPS stock and will be invested according to your pre-tax investment elections.'
If you have not made investment elections for your pre-tax contributions, the match will be invested into the age-appropriate Bright Horizon target date fund, the Plan’s default investment option.
When you retire, if you have balances in your 401(k) plan, you will receive a Participant Distribution Notice in the mail. This notice will show the current value that you are eligible to receive from each plan and explain your distribution options. It will also tell you what you need to do to receive your final distribution. Please call The Retirement Group at (800)-900-5867 for more information and we can get you in front of a retirement-focused advisor.
Next Steps:
- Watch for your Participant Distribution Notice and Special Tax Notice Regarding Plan Payments. These notices will help explain your options and what the federal tax implications may be for your vested account balance.
- "What has Worked in Investing" & "8 Tenets when picking a Mutual Fund".
- To learn about your distribution options, call The Retirement Group at (800)-900-5867. Click our e-book for more information on "Rollover Strategies for 401(k)s". Use the Online Beneficiary Designation to make updates to your beneficiary designations, if needed.
SavingsPLUS Match

Summary of Contribution Options (effective 1/1/2023)

After-Tax Contributions
Regular after-tax contributions are now be eligible for the SavingsPLUS match. For additional flexibility, you will be able to make separate investment elections for your after-tax contributions.
UPSers earning more than $150,000 a year (based on eligible compensation from the previous year) will no longer be eligible to make after-tax contributions in the 401(k) Plan to ensure total contributions do not exceed IRS limits.
Automatic Contribution Escalation
The auto escalation cap is being raised from 10% to 15% to help UPSers save even more. If you were previously auto-enrolled at a 6% pre-tax contribution and your contribution is being automatically escalated 1% each year, it will continue to escalate until you reach 15% or make an adjustment to your savings rate.
Over half of plan participants admit they don’t have the time, interest or knowledge needed to manage their 401(k) portfolio. But the benefits of getting help goes beyond convenience. Studies like this one, from Charles Schwab, show those plan participants who get help with their investments tend to have portfolios that perform better: The annual performance gap between those who get help and those who do not is 3.32% net of fees. This means a 45-year-old participant could see a 79% boost in wealth by age 65 simply by contacting an advisor. That’s a pretty big difference.
Getting help can be the key to better results across the 401(k) board.
A Charles Schwab study found several positive outcomes common to those using independent professional advice. They include:
- Improved savings rates – 70% of participants who used 401(k) advice increased their contributions.
- Increased diversification – Participants who managed their own portfolios invested in an average of just under four asset classes, while participants in advice-based portfolios invested in a minimum of eight asset classes.
- Increased likelihood of staying the course – Getting advice increased the chances of participants staying true to their investment objectives, making them less reactive during volatile market conditions and more likely to remain in their original 401(k) investments during a downturn. Don’t try to do it alone. Get help with your company's 401(k) plan investments. Your nest egg will thank you.
Eligible employees will receive the Retirement Contribution even if they do not make personal contributions to the 401(k) Plan.

Transition Contribution of 5% of the employee’s eligible compensation. This amount increases to 7% in 2028.
Example: UPSer who has 15 years of service and contributes 6% of Eligible Compensation to the 401(k) Plan.
Net Unrealized Appreciation (NUA)
When you qualify for a distribution, you have three options:
- Roll-over your qualified plan to an IRA and continue deferring taxes.
- Take a distribution and pay ordinary income tax on the full amount.
- Take advantage of NUA and reap the benefits of a more favorable tax structure on gains.
How does Net Unrealized Appreciation work?
First an employee must be eligible for a distribution from their qualified company-sponsored plan. Generally, at retirement or age 59 1⁄2, the employee takes a 'lump-sum' distribution from the plan, distributing all assets from the plan during a 1-year period. The portion of the plan that is made up of mutual funds and other investments can be rolled into an IRA for further tax deferral. The highly appreciated company stock is then transferred to a non-retirement account.
The tax benefit comes when you transfer the company stock from a tax-deferred account to a taxable account. At this time, you apply NUA and you incur an ordinary income tax liability on only the cost basis of your stock. The appreciated value of the stock above its basis is not taxed at the higher ordinary income tax but at the lower long-term capital gains rate, currently 15%. This could mean a potential savings of over 30%.
You may be interested in learning more about NUA with a complimentary one-on-one session with a financial advisor from The Retirement Group.
IRA Withdrawal
When you qualify for a distribution, you have three options:
Your retirement assets may consist of several retirement accounts: IRAs, 401(k)s, taxable accounts, and others.
So, what is the most efficient way to take your retirement income after leaving your company?
You may want to consider meeting your income needs in retirement by first drawing down taxable accounts rather than tax-deferred accounts.
This may help your retirement assets with your company last longer as they continue to potentially grow tax deferred.
You will also need to plan to take the required minimum distributions (RMDs) from any company-sponsored retirement plans and traditional or rollover IRA accounts.
That is due to IRS requirements for 2024 to begin taking distributions from these types of accounts when you reach age 73. Beginning in 2024, the excise tax for every dollar of your RMD under-distributed is reduced from 50% to 25%.
There is new legislation that allows account owners to delay taking their first RMD until April 1 following the later of the calendar year they reach age 73 or, in a workplace retirement plan, retire.
Two flexible distribution options for your IRA
When you need to draw on your IRA for income or take your RMDs, you have a few choices. Regardless of what you choose, IRA distributions are subject to income taxes and may be subject to penalties and other conditions if you’re under 59½.
Partial withdrawals: Withdraw any amount from your IRA at any time. If you’re 73 or over, you’ll have to take at least enough from one or more IRAs to meet your annual RMD.
Systematic withdrawal plans: Structure regular, automatic withdrawals from your IRA by choosing the amount and frequency to meet your income needs after retiring from your company. If you’re under 59½, you may be subject to a 10% early withdrawal penalty (unless your withdrawal plan meets Code Section 72(t) rules).
Your tax advisor can help you understand distribution options, determine RMD requirements, calculate RMDs, and set up a systematic withdrawal plan.
Your Benefits
HSA's
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) are often celebrated for their utility in managing healthcare expenses, particularly for those with high-deductible health plans. However, their benefits extend beyond medical cost management, positioning HSAs as a potentially superior retirement savings vehicle compared to traditional retirement plans like 401(k)s, especially after employer matching contributions are maxed out.
Understanding HSAs
HSAs are tax-advantaged accounts designed for individuals with high-deductible health insurance plans. For 2024, the IRS defines high-deductible plans as those with a minimum deductible of $1,600 for individuals and $3,200 for families. HSAs allow pre-tax contributions, tax-free growth of investments, and tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses—making them a triple-tax-advantaged account.
The annual contribution limits for HSAs in 2024 are $4,150 for individuals and $8,300 for families, with an additional $1,000 allowed for those aged 55 and older. Unlike Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs), HSA funds do not expire at the end of the year; they accumulate and can be carried over indefinitely.
Comparing HSAs to 401(k)s Post-Matching
Once an employer's maximum match in a 401(k) is reached, further contributions yield diminished immediate financial benefits. This is where HSAs can become a strategic complement. While 401(k)s offer tax-deferred growth and tax-deductible contributions, their withdrawals are taxable. HSAs, in contrast, provide tax-free withdrawals for medical expenses, which are a significant portion of retirement costs.
HSA as a Retirement Tool
Post age 65, the HSA flexes its muscles as a robust retirement tool. Funds can be withdrawn for any purpose, subject only to regular income tax if used for non-medical expenses. This flexibility is akin to that of traditional retirement accounts, but with the added advantage of tax-free withdrawals for medical costs—a significant benefit given the rising healthcare expenses in retirement.
Furthermore, HSAs do not have Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs), unlike 401(k)s and Traditional IRAs, offering more control over tax planning in retirement. This makes HSAs particularly advantageous for those who might not need to tap into their savings immediately at retirement or who want to minimize their taxable income.
Investment Strategy for HSAs
Initially, it's prudent to invest conservatively within an HSA, focusing on ensuring that there are sufficient liquid funds to cover near-term deductible and other out-of-pocket medical expenses. However, once a financial cushion is established, treating the HSA like a retirement account by investing in a diversified mix of stocks and bonds can significantly enhance the account's growth potential over the long term.
Utilizing HSAs in Retirement
In retirement, HSAs can cover a range of expenses:
- Healthcare Costs-Pre Medicare: HSA's Can pay for healthcare costs to bridge you to Medicare
- Healthcare Costs-Post Medicare: HSAs can pay for Medicare premiums and out-of-pocket medical costs, including dental and vision, which are often not covered by Medicare.
- Long-term Care: Funds can be used for qualified long-term care services and insurance premiums.
- Non-medical Expenses: After age 65, HSA funds can be used for non-medical expenses without incurring penalties, although these withdrawals are subject to income tax.
Conclusion
In summary, HSAs offer unique advantages that can make them a superior option for retirement savings, particularly after the benefits of 401(k) matching are maximized. Their flexibility in fund usage, coupled with tax advantages, makes HSAs an essential component of a comprehensive retirement strategy. By strategically managing contributions and withdrawals, individuals can maximize their financial health in retirement, keeping both their medical and financial well-being secure.
Your life insurance coverage and any optional coverage you purchase for your spouse/domestic partner and/or children ends on the date your employment with your company ends, unless your employment ends due to disability. If you die within 31 days of your termination date from your company, benefits are paid to your beneficiary for your basic life insurance, as well as any additional life insurance coverage you elected.
Note:
-
You may have the option to convert your life insurance to an individual policy or elect portability on any optional coverage.
-
If you stop paying supplementary contributions, your coverage will end.
-
If you are at least 65 and you pay for supplemental life insurance, you should receive information in the mail from the insurance company that explains your options.
-
Make sure to update your beneficiaries. See your company's SPD for more details.
Next Step:
- When you retire, make sure that you update your beneficiaries, and update the Beneficiary Designation form for life events such as death, marriage, divorce, childbirth, adoptions, etc.
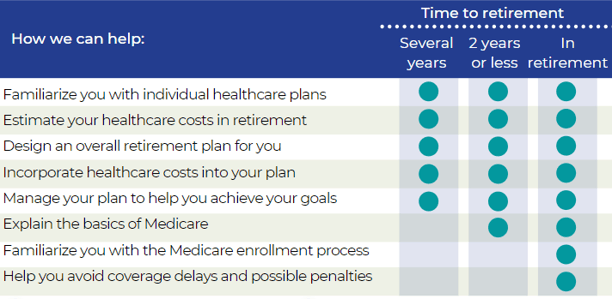
Social Security & Medicare

Knowing the foundation of Social Security, and using this knowledge to your advantage, can help you claim your maximum benefit.
It’s your responsibility to enroll in Medicare parts A and B when you first become eligible — and you must stay enrolled to have coverage for Medicare-eligible expenses. This applies to your Medicare eligible dependents as well.
You should know how your retiree medical plan choices or Medicare eligibility impacts your plan options. Before you retire from your company, contact the U.S. Social Security Administration directly at 800-772-1213, call your local Social Security Office or visit ssa.gov.

You and your Medicare-eligible dependents must enroll in Medicare Parts A and B when you first become eligible. Medical and MH/SA benefits payable under the company's-sponsored plan will be reduced by the amounts Medicare Parts A and B would have paid whether you actually enroll in them or not.

Divorce

If you’re divorced or in the process of divorcing, your former spouse(s) may have an interest in a portion of your retirement benefits from your company. Before you can start your pension — and for each former spouse who may have an interest — you’ll need to provide your company with the following documentation:
- A copy of the court-filed Judgment of Dissolution or Judgment of Divorce along with any Marital Settlement Agreement (MSA)
- A copy of the court-filed Qualified Domestic Relations Order (QDRO)
You were married for at least 10 years prior to the divorce.
You are currently unmarried.
Your ex-spouse is entitled to Social Security benefits.
Unlike with a married couple, your ex-spouse doesn’t have to have filed for Social Security before you can apply for your divorced spouse’s benefit.
Divorce doesn’t disqualify you from survivor benefits. You can claim a divorced spouse’s survivor benefit if the following are true:
- Your ex-spouse is deceased.
- You are at least 60 years of age.
- You were married for at least 10 years prior to the divorce.
- You are single (or you remarried after age 60).
In the process of divorcing?
If your divorce isn’t final before your retirement date from your company, you’re still considered married. You have two options:
- Retire from your company before your divorce is final and elect a joint pension of at least 50% with your spouse — or get your spouse’s signed, notarized consent to a different election or lump sum.
- Delay your retirement from your company until after your divorce is final and you can provide the required divorce documentation.*
Source: The Retirement Group, “Retirement Plans - Benefits and Savings,” U.S. Department of Labor, 2019; “Generating Income That Will Last Throughout Retirement,” Fidelity, 2019
Survivor Checklist

In the unfortunate event that you aren’t able to collect your benefits from your company, your survivor will be responsible for taking action.
What your survivor needs to do:
- Report your death. Your spouse, a family member or even a friend should call your company’s benefits service center as soon as possible to report your death.
- Collect life insurance benefits. Your spouse, or other named beneficiary, will need to call your company's benefits service center to collect life insurance benefits.
If you have a joint pension:
- Start the joint pension payments. The joint pension is not automatic. Your joint pensioner will need to complete and return the paperwork from your company's pension center to start receiving joint pension payments.
- Be prepared financially to cover living expenses. Your spouse will need to be prepared with enough savings to bridge at least one month between the end of your pension payments from your company and the beginning of his or her own pension payments.
If your survivor has medical coverage through your company:
- Decide whether to keep medical coverage.
- If your survivor is enrolled as a dependent in your company-sponsored retiree medical coverage when you die, he or she needs to decide whether to keep it. Survivors have to pay the full monthly premium.
Life After Your Career

Make up for decreased value of savings or investments. Low interest rates make it great for lump sums but harder for generating portfolio income. Some people continue to work to make up for poor performance of their savings and investments.
Maybe you took an offer from your company and left earlier than you wanted with less retirement savings than you needed. Instead of drawing down savings, you may decide to work a little longer to pay for extras you’ve always denied yourself in the past.
Meet financial requirements of day-to-day living. Expenses can increase during your retirement from your company and working can be a logical and effective solution. You might choose to continue working in order to keep your insurance or other benefits — many employers offer free to low cost health insurance for part-time workers.
You might find yourself with very tempting job opportunities at a time when you thought you’d be withdrawing from the workforce.
Staying active and involved. Retaining employment after your previous job, even if it’s just part-time, can be a great way to use the skills you’ve worked so hard to build over the years and keep up with friends and colleagues.
Enjoying yourself at work. Just because the government has set a retirement age with its Social Security program doesn’t mean you have to schedule your own life that way. Many people genuinely enjoy their employment and continue working because their jobs enrich their lives.
Sources
6.png)
- “National Compensation Survey: Employee Benefits in the United States, March 2019," Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor.
- “Generating Income That Will Last throughout Retirement.” Fidelity, 22 Jan. 2019, www.fidelity.com/viewpoints/retirement/income-that-can-last-lifetime.
- “Retirement Plans-Benefits & Savings.” U.S. Department of Labor, 2019, www.dol.gov/general/topic/retirement.
- AT&T Summary Plan Description, 2019
- Chevron Summary Plan Description, 2019
- Shell Summary Plan Description, 2019
- ExxonMobil Summary Plan Description, 2019
- https://seekingalpha.com/article/4268237-order-withdrawals-retirement-assets
- https://www.aon.com/empowerresults/ensuring-retirees-get-health-care-need/
- 8 Tenets when picking a Mutual Fund e-book
- Determining Cash Flow Need in Retirement e-book
- Early Retirement Offers e-book
- Lump Sum vs. Annuity e-book
- Social Security e-book
- Rising Interest Rates e-book
- Closing The Retirement Gap e-book
- Rollover Strategies for 401(k)s e-book
- How to Survive Financially After a Job Loss e-book
- Financial PTSD e-book
- RetireKit
- What has Worked in Investing e-book
- Retirement Income Planning for ages 50-65 e-book
- Strategies for Divorced Individuals e-book
- TRG Webinar for Corporate Employees
- Composite Corp Bond Rate history (10 years)http://www.irs.gov/retirement/article/0,,id=123229,00.html https://www.irs.gov/retirement-plans/composite-corporate-bond-rate-table
- IRS 72(t) code: https://www.irs.gov/retirement-plans/plan-participant-employee/retirement-topics-tax-on-early-distributions
- Missing out: How much employer 401(k) matching contributions do employees leave on the table?
- Jester Financial Technologies, Worksheet Detail - Health Care Expense Schedule
- Social Security Administration. Benefits Planner: Income Taxes and Your Social Security Benefits. Social Security Administration. Retrieved October 11, 2016 from https://www.ssa.gov/planners/taxes.html
- http://hr.chevron.com/northamerica/us/payprograms/executiveplans/dcp/
- https://www.lawinsider.com/contracts/1tRmgtb07oJJieGzlZ0tjL/chevron-corp/incentive-plan/2018-02-02
-
https://www.irs.gov/newsroom/irs-provides-tax-inflation-adjustments-for-tax-year-2022
-
https://news.yahoo.com/taxes-2022-important-changes-to-know-164333287.html
-
https://www.nerdwallet.com/article/taxes/federal-income-tax-brackets
-
https://www.the-sun.com/money/4490094/key-tax-changes-for-2022/
-
https://www.bankrate.com/taxes/child-tax-credit-2022-what-to-know/